Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a comprehensive approach to managing and analyzing security data within an organization. It combines two key functions:

- Security Information Management (SIM): This focuses on collecting and storing security data from various sources, such as logs from network devices, servers, and applications. SIM involves data aggregation, normalization, and historical analysis to identify trends and potential issues over time.
- Security Event Management (SEM): This deals with real-time monitoring and analysis of security events. SEM systems detect and respond to potential threats by analyzing data in real-time, generating alerts, and enabling security teams to take immediate action.
Exeon
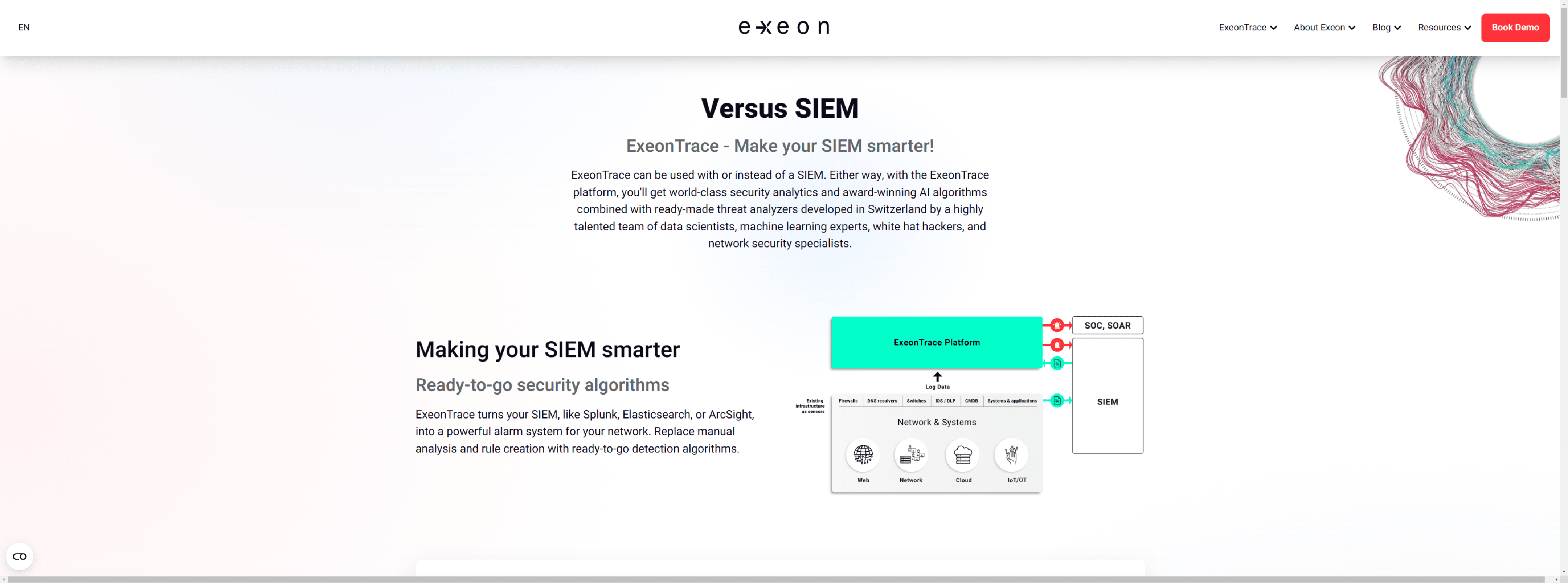
ExeonTrace with or instead of a SIEM to efficiently and effectively monitor traffic across your entire IT/OT network.
- High-performance software collectors to collect very large amounts of system data. Eliminating the need for hardware sensors
- Powerful AI to create source-specific enriched security data
- Dedicated and intuitive visualizations for the respective data sources and their use cases
- Ready-made analyzer algorithms and use cases designed specifically for the respective data sources and their security scenarios
- Optimized investigation views and guided threat hunting for the respective data sources and their use cases
Solarwinds
Improve your security posture with an easy-to-use, affordable SolarWinds Security Event Manager (formerly Log & Event Manager).
- Centralized log collection and normalization
- Automated threat detection and response
- Integrated compliance reporting tools
- Intuitive dashboard and user interface
- Built-in file integrity monitoring
- Simple and affordable licensing
Logrhythm
LogRhythm provides cybersecurity solutions such as SIEM, SOAR, UEBA, and NDR to help organizations detect, investigate, and respond to cyberattacks.
- Value for security and IT operations
- Broad integration across security and IT vendors
- Compliance adherence and reporting
Trellix
Future-proof your SIEM using Trellix Security Operations and integrate existing security tools with our XDR ecosystem.
- Accelerate incident response
- Keep ahead of cyberthreats
- Unify your security tools
Elastic
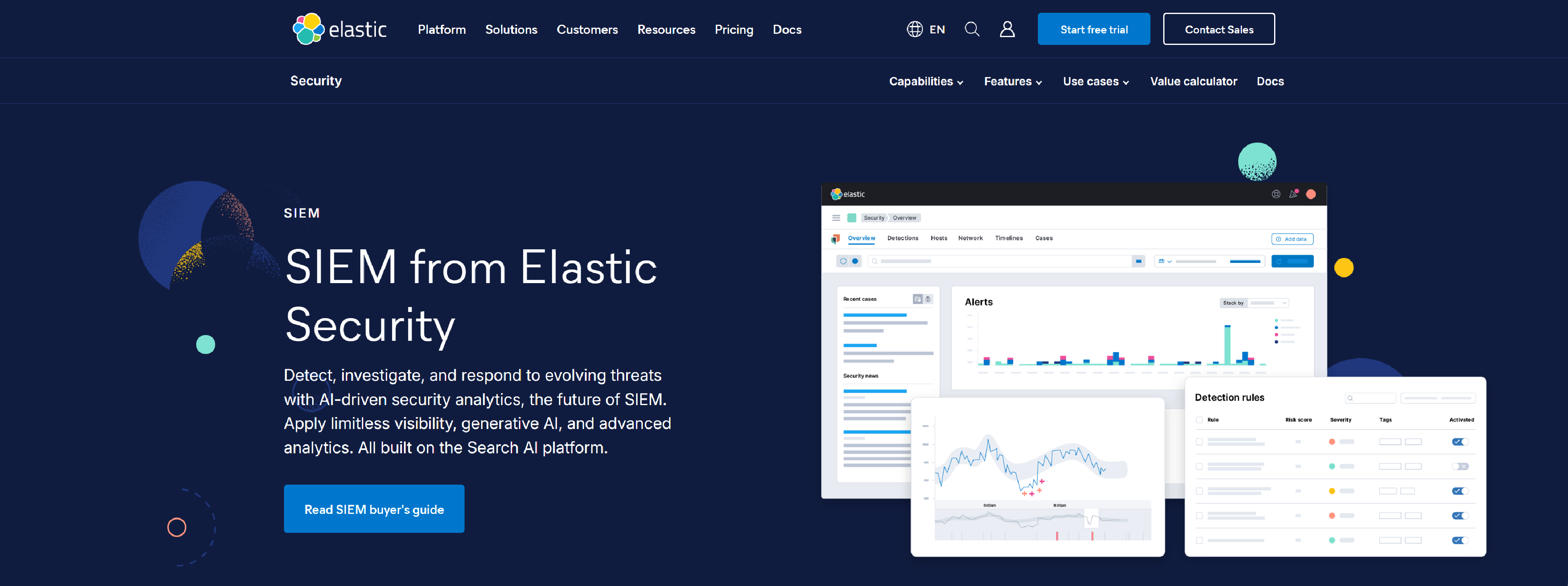
Elastic Security for SIEM is fueled by AI-driven security analytics, equipping the SOC to detect, investigate, and respond to advanced threats.
- Analyze your enterprise at will
- Expedite detection and triage
- Assess risk with ML and advanced entity analytics
- Streamline investigation, automate response
Fortinet
FortiSIEM is designed to be the backbone of your security operations team, delivering capabilities ranging from automatically building your inventory of assets to applying cutting edge behavioral analytics to rapidly detect and respond to threats.
- Self-Learning Asset Inventory
- Real-Time Security Analytics
- Powered by Generative AI
- Osquery Endpoint Visibility
- Deep Fabric Integration
- Industry-Leading Threat Intelligence
Rapid7
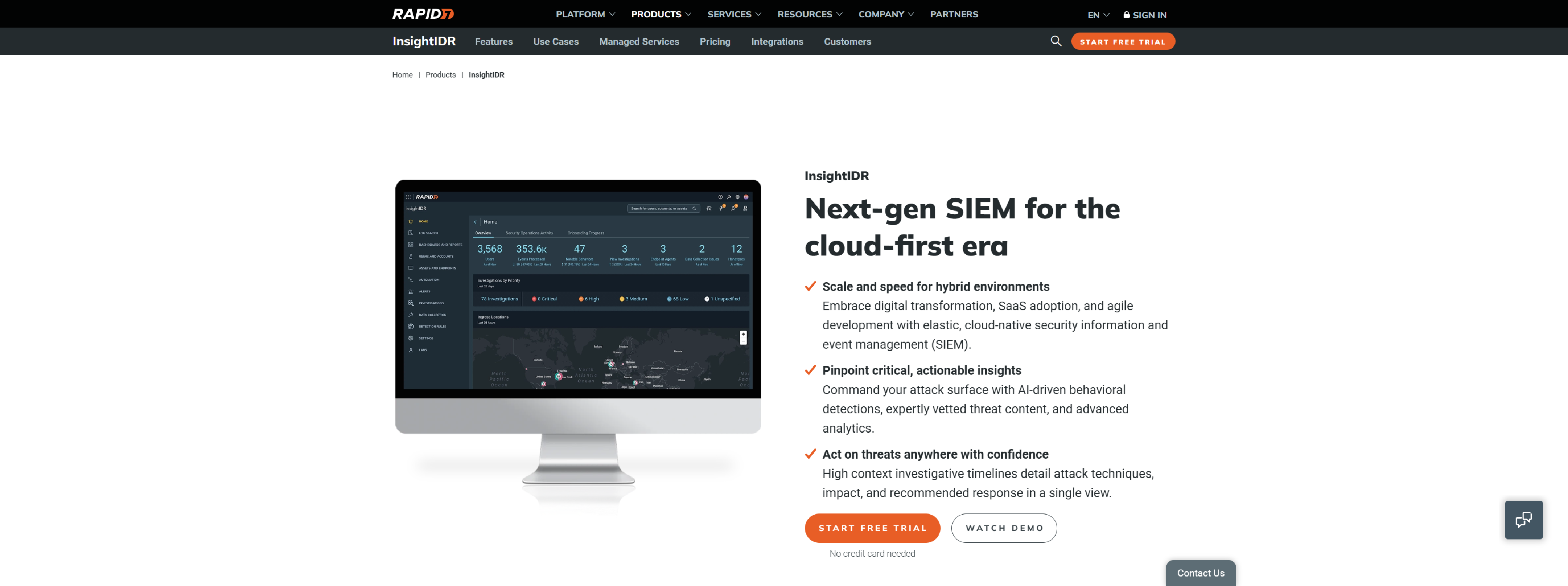
Rapid7 next-gen security information and event management (SIEM) solution for a cloud-first era.
- Work with a Gartner Magic Quadrant Challenger
- Achieve faster time-to-value
- Level up your analysis easily
- Eliminate security and compliance silos
What is the purpose of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
The purpose of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is to provide organizations with a comprehensive solution for managing and analyzing security-related data. SIEM aims to enhance an organization’s ability to detect, respond to, and mitigate security threats and incidents. Here are the key purposes of SIEM:
1. Centralized Data Collection
SIEM systems aggregate security-related data from diverse sources, such as network devices, servers, applications, and security tools, into a unified platform. This centralized collection simplifies the management of security data and provides a holistic view of the organization’s security posture.
2. Real-Time Threat Detection
By continuously monitoring and analyzing data in real-time, SIEM systems can identify and alert on potential security threats and incidents. This enables organizations to detect suspicious activities or anomalies as they occur, allowing for prompt response and mitigation.
3. Incident Response
SIEM facilitates efficient incident response by providing detailed information and context about security events. When a potential threat is detected, SIEM can generate alerts, provide relevant data, and help security teams investigate and address the incident effectively.
4. Data Correlation and Analysis
SIEM systems correlate data from multiple sources to identify patterns and relationships that may indicate a security threat. This correlation helps in detecting complex attack vectors that may not be apparent when looking at individual data sources in isolation.
5. Compliance and Reporting
Many organizations are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate the logging and reporting of security-related events. SIEM helps organizations meet these compliance requirements by providing tools for generating detailed reports, audit trails, and documentation.
6. Threat Intelligence Integration
SIEM systems often integrate with threat intelligence feeds to enhance their ability to detect known threats. By incorporating external threat intelligence, SIEM can provide more accurate and contextually relevant alerts.
7. Historical Data Analysis
SIEM systems store and analyze historical security data, allowing organizations to track long-term trends, investigate past incidents, and understand how security threats evolve over time.
8. Security Posture Improvement
Through ongoing monitoring, analysis, and reporting, SIEM helps organizations assess and improve their overall security posture. It provides insights into potential vulnerabilities, helps refine security policies, and supports strategic decision-making.
What are the benefits of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) offers several key benefits to organizations by enhancing their ability to manage and respond to security threats. Here’s a breakdown of the primary advantages:
Improved Threat Detection and Response
- Real-Time Monitoring: SIEM systems provide continuous monitoring and analysis of security events, allowing for the rapid detection of potential threats and anomalies.
- Automated Alerts: SIEM can generate alerts based on predefined rules and correlations, enabling security teams to quickly address potential security incidents.
Enhanced Visibility and Insight
- Centralized Data Aggregation: By consolidating data from various sources such as network devices, servers, and applications, SIEM offers a unified view of the organization’s security landscape.
- Comprehensive Reporting: SIEM tools provide detailed dashboards and reports that help security teams understand trends, patterns, and potential vulnerabilities.
Efficient Incident Management
- Contextual Information: SIEM systems provide context around security events, helping teams investigate and respond to incidents more effectively.
- Incident Tracking: It helps in managing the lifecycle of security incidents, from detection through investigation to resolution.
Enhanced Security Posture
- Correlation and Analysis: SIEM systems correlate data from multiple sources to identify complex attack patterns and potential security threats that may not be apparent in isolated data.
- Proactive Threat Hunting: With historical data and trend analysis, SIEM facilitates proactive threat hunting and helps in identifying potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Compliance and Reporting
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries have specific regulatory requirements for data security and privacy. SIEM helps organizations meet these requirements by providing detailed logging, reporting, and audit trails.
- Audit Readiness: SIEM tools streamline the process of generating compliance reports and demonstrating adherence to security standards and regulations.
Operational Efficiency
- Automated Processes: SIEM automates many security monitoring tasks, reducing the manual effort required from security teams and allowing them to focus on more strategic activities.
- Integration with Other Tools: SIEM systems often integrate with other security solutions, such as threat intelligence platforms and incident response tools, to enhance overall security operations.
Historical Data Analysis
- Trend Identification: SIEM systems store historical data, which helps in identifying long-term trends and understanding how security threats evolve over time.
- Post-Incident Analysis: Historical data enables detailed post-incident analysis, helping organizations learn from past incidents and improve their security measures.
Enhanced Threat Intelligence
Integration with Threat Feeds: Many SIEM systems integrate with external threat intelligence feeds to provide up-to-date information on known threats, vulnerabilities, and attack techniques.
SIEM provides organizations with a robust framework for detecting and responding to security threats, enhancing overall visibility into security events, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. By centralizing data, automating threat detection, and improving incident management, SIEM helps organizations strengthen their security posture and operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is SIEM software?
A1: SIEM software is a solution that combines Security Information Management (SIM) and Security Event Management (SEM) to provide a comprehensive approach to monitoring, analyzing, and responding to security events within an organization. It collects data from various sources, analyzes it in real-time, and generates alerts to help identify and manage potential security threats.
Q2: How does SIEM software work?
A2: SIEM software works by collecting and aggregating logs and security data from various sources, such as network devices, servers, applications, and security tools. It normalizes this data into a common format, correlates events to identify patterns or anomalies, and generates alerts based on predefined rules or behavioral analysis. The software also provides reporting and visualization tools to help security teams understand and respond to security incidents.
Q3: What are the main components of SIEM software?
A3: The main components of SIEM software include:
- Data Collection: Gathers log and event data from various sources.
- Data Aggregation: Centralizes and consolidates data for analysis.
- Data Normalization: Converts data into a consistent format.
- Event Correlation: Analyzes data to identify patterns and relationships.
- Alerting: Generates notifications for potential security incidents.
- Incident Management: Provides tools for managing and responding to security events.
- Reporting and Dashboards: Offers visualizations and reports for monitoring and compliance.
Q4: What are the key benefits of using SIEM software?
A4: Key benefits of SIEM software include:
- Real-Time Threat Detection: Enables quick identification of potential threats.
- Enhanced Visibility: Provides a comprehensive view of security events across the organization.
- Efficient Incident Response: Facilitates quick and informed responses to security incidents.
- Compliance: Helps meet regulatory requirements by providing detailed logging and reporting.
- Operational Efficiency: Automates many security monitoring tasks, improving overall efficiency.
Q5: What types of organizations benefit from SIEM software?
- A5: SIEM software benefits a wide range of organizations, from small businesses to large enterprises. It is particularly valuable for:
- Regulated Industries: Organizations in sectors like finance, healthcare, and government that have stringent compliance requirements.
- Large Enterprises: Companies with complex IT environments and extensive security needs.
- Organizations with High Security Needs: Entities that need advanced threat detection and response capabilities due to the nature of their operations or the sensitivity of their data.
Q6: How does SIEM software differ from other security solutions?
A6: SIEM software differs from other security solutions in that it focuses on centralizing and correlating data from various sources to provide a comprehensive view of security events. While other solutions like firewalls or antivirus software may focus on specific types of threats or protection mechanisms, SIEM software provides broader visibility and context by aggregating data from across the entire IT environment.
Q7: Can SIEM software be used in the cloud?
A7: Yes, many SIEM solutions are available in cloud-based versions, offering flexibility and scalability. Cloud-based SIEM solutions can be particularly advantageous for organizations with dynamic environments or those looking to reduce the burden of managing on-premises infrastructure. These solutions often provide similar functionalities as on-premises systems but with the added benefits of cloud computing, such as easier scalability and lower upfront costs.
How much do Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Software typically cost?
The cost of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) software can vary widely based on several factors, including the size of the organization, the scale of deployment, the specific features required, and whether the solution is cloud-based or on-premises. Here’s a general breakdown of the potential costs:
1. Initial Costs:
- Licensing Fees: SIEM software is typically licensed either by the amount of data ingested, the number of log sources, or the number of users. For on-premises solutions, licensing can be a significant upfront cost.
- Implementation and Setup: Costs for professional services to deploy and configure the SIEM solution. This can include initial setup, integration with other systems, and customization.
2. Ongoing Costs:
- Subscription Fees: For cloud-based SIEM solutions, you’ll typically pay a subscription fee based on data volume, number of users, or other metrics.
- Maintenance and Support: Annual maintenance and support fees, which may cover updates, technical support, and troubleshooting.
- Data Storage: Costs related to storing historical data, which can be substantial depending on the volume and retention period.
3. Additional Costs:
- Training: Costs for training staff to use and manage the SIEM system effectively.
- Upgrades: Periodic upgrades or additional features may involve additional costs.
- Integration: Costs associated with integrating SIEM with other security tools and IT systems.
Cost Estimates:
Small to Mid-Sized Organizations: For smaller organizations or those with less demanding requirements, SIEM solutions might start around $10,000 to $50,000 annually for a basic subscription or licensing. Cloud-based options may have lower initial costs but could incur higher recurring fees based on data volume.
Large Enterprises: For larger organizations or those with extensive needs, the costs can range from $100,000 to several million dollars annually. This range covers comprehensive on-premises solutions, extensive data ingestion, and advanced features.
Cloud-Based SIEM Solutions: Generally offer flexible pricing models based on data volume and the number of users. Monthly fees can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands, depending on the scale and complexity of the deployment.